Blog
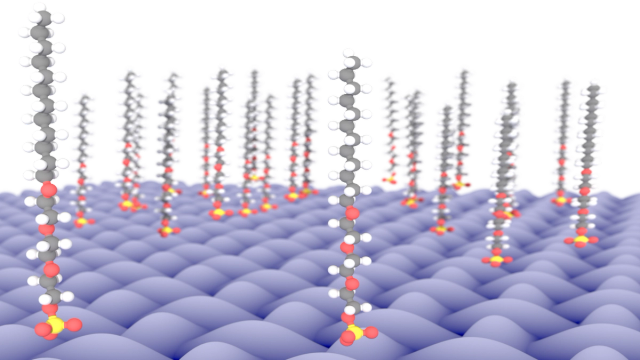
Additives for improved performance of detergents: Optimizing surfactants with simulation
July 15, 2025
Blog

How Digitalization and Sustainability go hand-in-hand in chemical R&D
May 5, 2025
Blog

Accelerating Polymer R&D: The future of research
April 2, 2025
Blog

What is Computational Chemistry? How it’s transforming chemical R&D
March 19, 2025
Blog
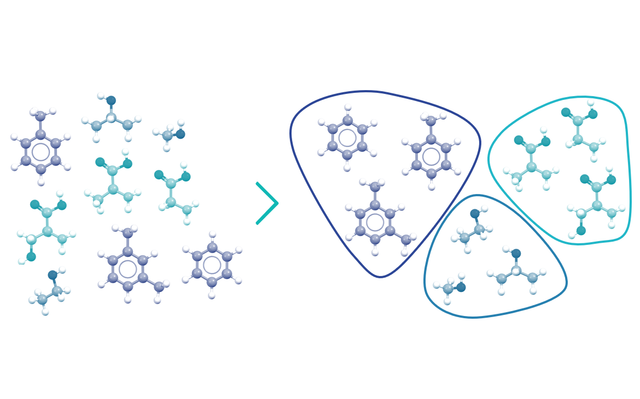
Data-driven discovery of new chemicals
January 28, 2025
Blog
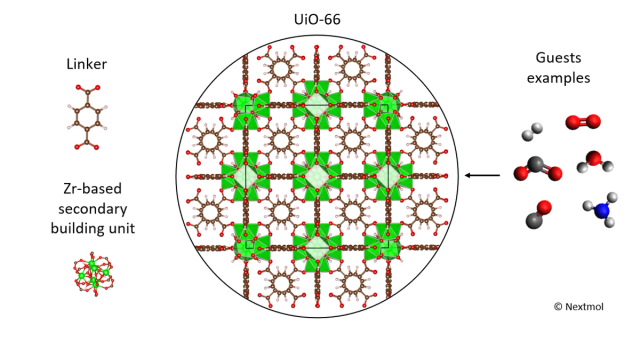
Computational development of metal-organic frameworks for sustainability
October 15, 2024
Blog
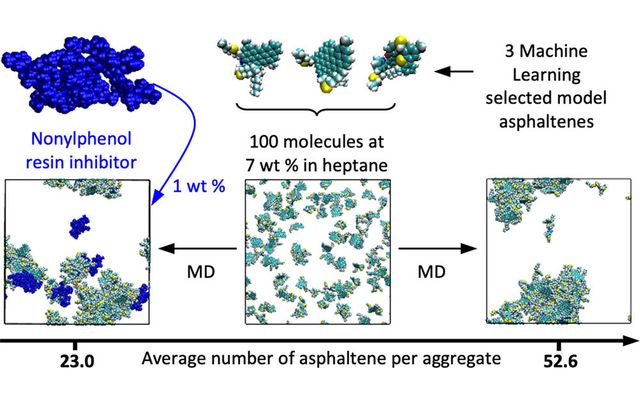
In silico evaluation of asphaltene inhibitor performances
July 23, 2024
Blog

Surfactants for Flow Assurance: Adsorption study via Molecular Modeling
April 10, 2024
Blog
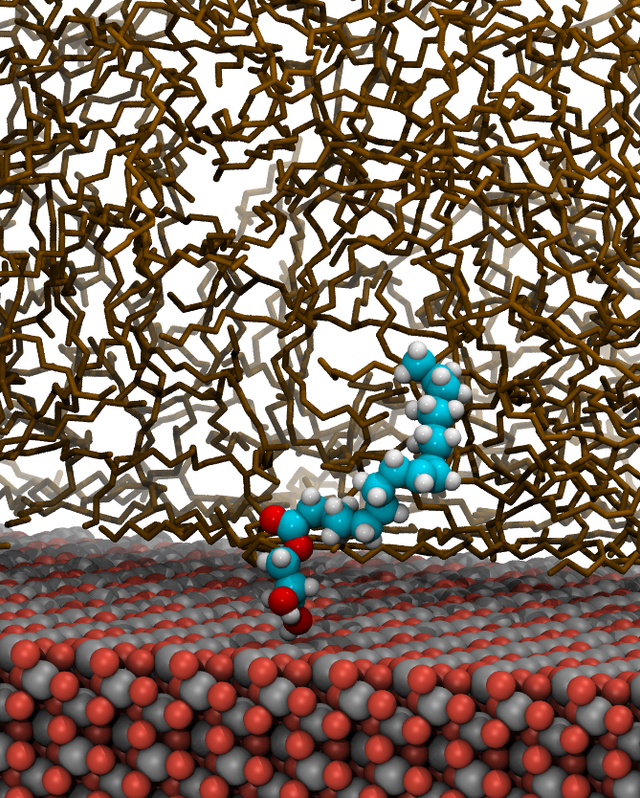
Lubricant additives: Adsorption
January 22, 2024
Blog
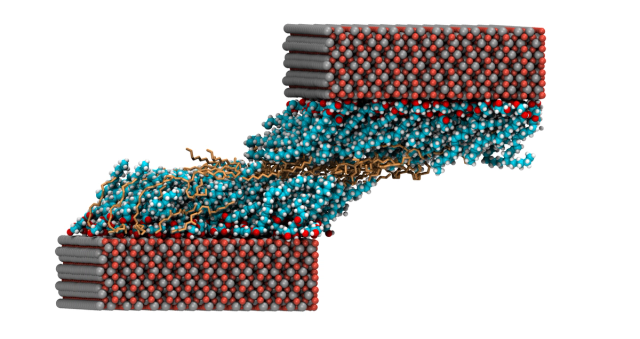
Lubricant additives: Friction modifiers
December 12, 2023
Blog
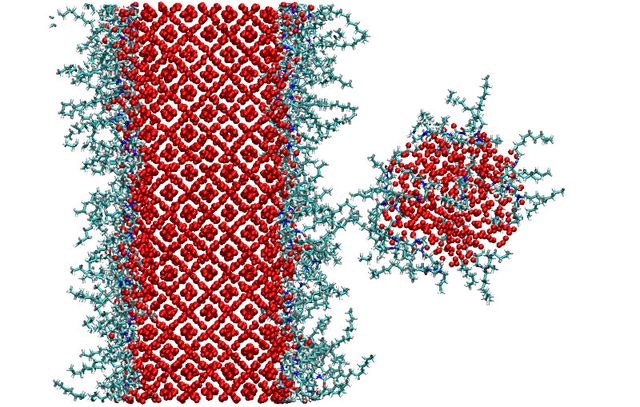
Molecular modeling of anti-agglomerants for Oil & Gas applications
October 5, 2023